

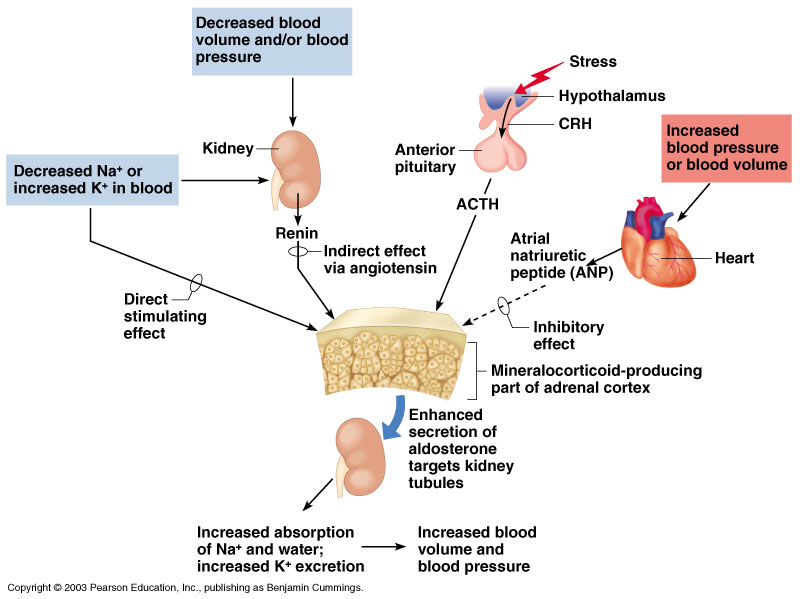
The medulla is stimulated to secrete the amine hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine. The sympathomedullary (SAM) pathway involves the stimulation of the medulla by impulses from the hypothalamus via neurons from the thoracic spinal cord. It is really an extension of the autonomic nervous system, which regulates homeostasis in the body. The adrenal medulla is neuroendocrine tissue composed of postganglionic sympathetic nervous system (SNS) neurons. This pathway will be discussed in more detail below. ACTH then stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce the hormone cortisol. The HPA axis involves the stimulation of hormone release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the pituitary by the hypothalamus. The adrenal cortex, as a component of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, secretes steroid hormones important for the regulation of the long-term stress response, blood pressure and blood volume, nutrient uptake and storage, fluid and electrolyte balance, and inflammation. Each region secretes its own set of hormones. The cortex itself is divided into three zones: the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata, and the zona reticularis. The adrenal gland consists of an outer cortex of glandular tissue and an inner medulla of nervous tissue.

View the University of Michigan WebScope to explore the tissue sample in greater detail. (Micrograph provided by the Regents of University of Michigan Medical School © 2012) The cortex can be subdivided into additional zones, all of which produce different types of hormones. Both adrenal glands sit atop the kidneys and are composed of an outer cortex and an inner medulla, all surrounded by a connective tissue capsule. Adrenal hormones are released into the circulation via the left and right suprarenal veins. Blood flows to each adrenal gland at the adrenal cortex and then drains into the adrenal medulla. They are served by several arteries branching off the aorta, including the suprarenal and renal arteries. The adrenal glands have a rich blood supply and experience one of the highest rates of blood flow in the body. The adrenal glands are wedges of glandular and neuroendocrine tissue adhering to the top of the kidneys by a fibrous capsule (Figure 1). Identify the hormones produced by the adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla, and summarize their target cells and effects.Describe the location and structure of the adrenal glands.\)īy the end of this section, you will be able to:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
